The SDK can be found here: https://github.com/nuubit/SDK/
Self Service Signup: https://portal.nuubit.net/#/signup/plans
The nuu:bit Mobile SDK is a simple way to connect a mobile application to nuu:bit's global content acceleration and analytics platform.
The nuu:bit Mobile SDK (Software Development Kit) is a set of libraries that provide the means necessary to report and accelerate the delivery of content to applications running on mobile devices. The nuu:bit SDK utilizes a specially designed set of networking protocols to provide acceleration to a given mobile application. Network traffic that is normally directed to and from the mobile App is sent through the nuu:bit SDK, which utilizes nuu:bit’s global network to accelerate the App’s traffic.
The SDK can function utilizing either of two nuu:bit-optimized protocols – an UDP-based protocol NMP (nuu:bit Mobile Protocol) or TCP-based protocol DOTS (Dynamically Optimized Transport System) to transfer the content over the wireless network. The SDK determines, which protocol provides better performance for that particular App, device, and wireless network at that moment in time. Once the appropriate protocol is selected, the protocol then senses network, device and App conditions, and adapts its own behavior in real time to provide the fastest possible transfer of data overall.
The nuu:bit SDK communicates with the nuu:bit server in the nuu:bit network, maintaining the flow of content, and monitoring and reporting on the operation of the SDK while sending performance data reflecting data transfer rates, bandwidth, latencies, etc. This raw data is then forwarded to nuu:bit log servers, and processed for reporting purposes. Processed data is then forwarded to the nuu:bit analytics backend service, where the performance information is made available to nuu:bit customers via the API or portal.
Why is the SDK needed?
Performance
While cellular network operators claim that user bandwidth has been increased in 4G-LTE, there are some indications that in many cases the latency experienced by users has actually increased. Many analysts have concluded that these cellular networks are congested, resulting in high latencies and less bandwidth utilization than potentially available.
In any event, here is available and unused bandwidth in most cellular networks, even while congested, and much of this is due to inefficiencies of conventional TCP and peculiarities of the cellular network as described in part in the following sections. What is needed is a properly designed networking protocol that can adaptively and intelligently navigate through these networks and utilize the unused bandwidth, and thereby decrease total round-trip delays.
The nuu:bit SDK helps mitigate the impact of congestion by using and optimizing UDP and TCP for the acceleration of content.
The SDK provides the following transport enhancements:
- Optimized data transport -- for faster speeds in both downlink and uplink directions
- Reliable transport – detects and handles packet loss efficiently, orders packets properly
- Minimal protocol overhead -- for session establishment,both in connection start-up and in continuous operation
- No teardown of connection due to cellular radio state transitions (without ongoing power requirements) or transfers to neighboring cell sites
- TLS/SSL support using X.509v3 certificates
- Transparent penetration of cellular network middle-boxes -- operates without interference from middle boxes in the cellular network.
- Encryption/decryption of headers and payload as with SSL
- Port “spoofing”
- Header/payload compression
- Session performance data can be recorded and utilized to optimize subsequent transport sessions to the same client
- Environment-agnostic performance improvements -- Operates equally well in wired environments, accelerating data transport over that provided by conventional TCP
Visibility
Another problem the nuu:bit SDK solves is the lack of end-to-end visibility of an App’s performance. nuu:bit provides this visibility by combining network, transactions and device metric and analytics into a single interface.
The nuu:bit mobile analytics interface offer reporting dashboards for daily active users (DAU), monthly active users (MAU) and average request time (processing). There are multiple pie charts which will display user count, request count and gigabytes transferred. The pie charts can be available for geographies, mobile devices, operating systems and per carrier. Also available is the ratio between Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
Top-object reports for the following aggregations:
- Top requests
- Top objects with slowest response time
- Top objects with slowest TTFB
- Top objects with 404 responses
- Top objects with 5xx responses
- Top objects with cache misses
- Top objects with completion failures
How it works
Once the SDK is compiled into the App, the nuu:bit SDK has three operating modes: Report, Transfer, and Transfer Plus Report.
When the mode is set to Transfer, the SDK works by intercepting NSURL calls. AFNetworking, NSCache, RestKit as well as anything built on NSurl will all be intercepted. The SDK allows configuration for what domains and/or sites are intercepted. By default, all requests are intercepted and sent to the nuu:bit edge using DOTS or NMP.
The SDK reporting function will report numerous App, wireless and handset details. The amount of reporting is configurable via the nuu:bit Portal or API. The controls at a high level are for handset reporting interval, log level and number of requests per report. Reporting interval is the period of time between when the analytics are sent to the device. The log level is the levels of detail with debug level being the most detailed. The number of requests per report is the number of user data requests is performed before sending the analytics to nuu:bit.
There are three separate data streams between the nuu:bit edge and the handset. This is shown in Figure 1. The data path for the App data is the first. This uses nuu:bit’s NMP or DOTS for acceleration of the content delivery. The second data stream is the SDK control telemetry. Using the nuu:bit portal or APIs, different configuration parameters can be sent to the nuu:bit SDK over this stream. The controls are for reporting, data interception and other SDK features. Last data stream is for analytics. The analytics are sent from the handset to the nuu:bit edge, collected and combined with the proxy HTTP log data, thus providing end-to-end visibility.
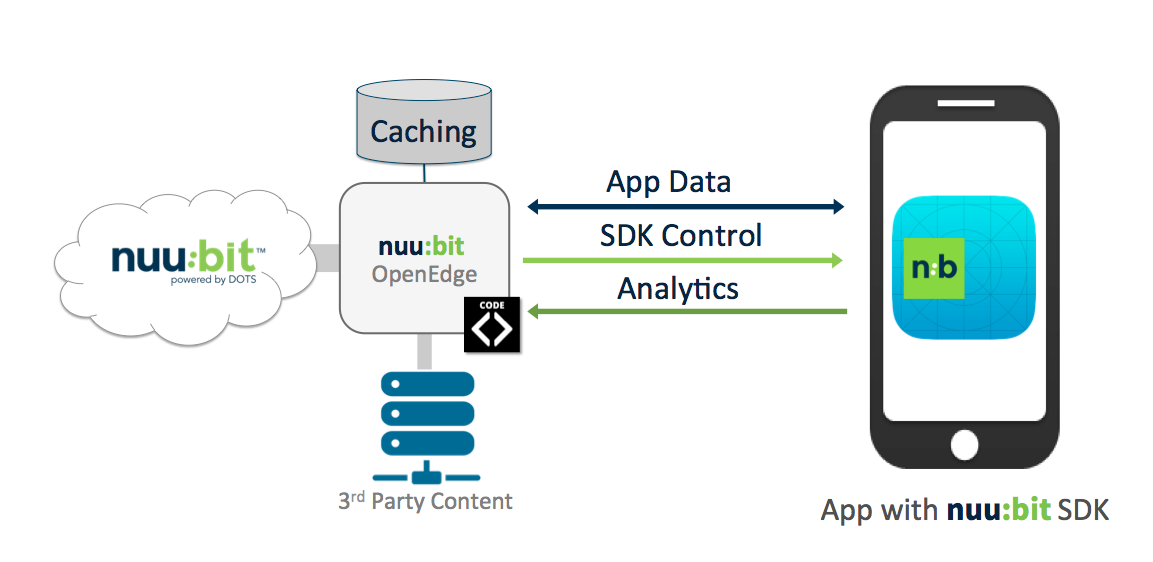
Detailed last mile diagram - Figure 1
The control and analytics streams are sent to the nuu:bit backend.While App data stream is set to the nuu:bit edge, depending on the request, the requested object may be a cache hit, dynamic which is requested from origin or pulled from a 3rd party provider.
For non-dynamic content, nuu:bit does offer edge caching and the ability for custom VCL rules for complex applications. nuu:bit supports instant purging of objects via the nuu:bit portal and APIs. 3rd party content can also be pulled depending on the configuration of the SDK. By default, all requests, including 3rd party requests sent to the nuu:bit edge where the objects are requested from their origin(s). nuu:bit will cache 3rd party objects based on the cache headers of the specific object. The end to end data flow can be seen in Figure 2.
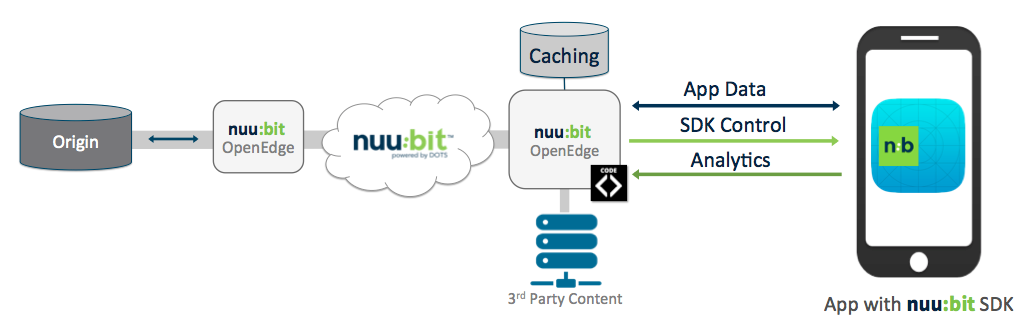
End-to-End diagram - Figure 2

0 Comments